Parametric Modeling of Spider Orb Web
Project 1 Objectives:
- Construct the web based on parametric tools in Grasshopper
- Apply uniform force (e.g. gravity) to model dynamic of constructed web
Project 2 Objectives:
- Model the localized force on the web (e.g. randomly hitting objects
Results on Project 1
Preliminaries
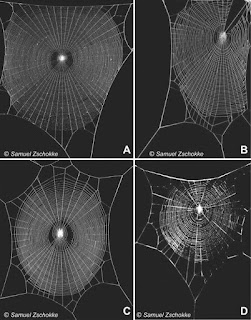
- Examples on spider orb webs in nature
Fig. 1. (A) Zilla diodia. (B) Zygiella x-notata. (C) Araneus diadematus. (D) Cyclosa oculata. Secondary frames can be seen in (A) to (D). Radials with Y-structure can be seen in (C). Spiders avoid connecting radials to the frame near an anchor, and close proximity between the ends of contiguous secondary frame threads. Courtesy of Dr. Samuel Zschokke (University of Basel).
Fig. 2. Some parameters that can be applied to model the web
Grasshopper Model
- Lines from polygon center to its vertices
- Construct spiral curve
- Construct straight lines from intersection points
- Subdivides the curves to enhance the spring system model
- Merge all the components to form the model & select the set of anchor points and
- Assign the particle/spring system and Kangaroo physics engine
- Run the model to see the dynamic of designed web
- The location of steps above in grasshopper model.
Grasshopper Model Movie I
Project 2 Objectives:
- Model the localized force on the web (e.g. randomly hitting objects
- Assign particle system
- Calculate the hitting force (it will be active when the particle hits the net)
Grasshopper Model Movie II















Comments
Post a Comment